A Short History Of Life On Earth (Abecedarian) Poem by Spock the Vegan
A Short History Of Life On Earth (Abecedarian)
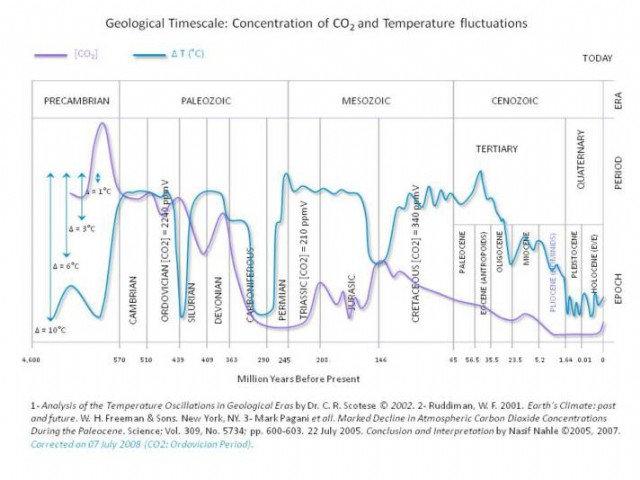
Precambrian Era (4600 to 542.0 million years ago)
A permanent record of the Earth's past is marked by the
Boundaries of different layers of sedimentary rock which
Contains fossilized remains of plants and animals laid
Down over millions of years. Precambrian is the first of
Earth's geologic ages. The Precambrian age is by
Far the longest, starting 4.5 billion years ago. It is believed a
Global ice age was near its end causing extinctions of life that
Harnessed the sun's power through photosynthesis. This
Ice age may have may have changed the mix of a complex
Jackpot of multi-celled life-forms, with many that were
Killed off to start the Cambrian Period.
Levels of oxygen gradually climbed in the atmosphere from
Microscopic cyanobacteria, reaching about one percent
Nearly two billion years ago. About 800 million years ago,
Oxygen levels rose to about 21 percent (like today) by
Photosynthesis from the cyanobacteria.
Quests to find out about this period have shown that the oxygen-
Rich ozone layer was also established which
Shields the Earth from harmful solar radiation.
This laid the groundwork to
Usher in the Cambrian and the rest of the Paleozoic with their
Various life forms.
Cambrian Period (542.0 to 488.3 mya)
A dramatic burst of evolutionary changes in life on Earth
Became known as the 'Cambrian Explosion.' Some resembled
Clams, and there were arthropods and chordates (animals with a
Dorsal nerve cord) . This period lasted about 53 million years of
Earth's history. The end of this period is marked by evidence in the
Fossil record of a mass extinction event about 490 million years ago.
Glaciers and a colder climate may have been the cause.
Ordovician Period (488.3 to 443.7 mya)
Algae and sponges dominated reef ecosystems and sometimes by
Bryozoans. However, there apparently were also periods of
Complete reef collapse due to global disturbances.
Diverse marine life was here, including graptolites, trilobites and
Early vertebrates, and brachiopods. There were also primitive
Fish, cephalopods, corals, crinoids, and gastropods, plus red and
Green algae. Tetrahedral spores similar to those of primitive land plants
Have been found, suggesting that plants invaded the land at this time.
Invertebrate genera and 25% of all families went extinct.
Silurian Period (443.7 to 416.0 mya)
About 443.7 to 416.0 million years ago was a time when many
Biologically significant events occurred. In the oceans, there were
Crinoids spreading widely and proliferation of the brachiopods.
Deglaciation and rise in sea levels created many new marine habitats.
Erratic climatic fluctuations ended for a time and coral reefs made their
First appearance during this time.
Devonian Period (416.0 to 359.2 mya)
All through the Devonian period, the seas were dominated by
Brachiopods, such as the spiriferids, and by tabulate and rugose
Corals, which built large reefs in shallow waters. In the Lower
Devonian, ammonoids appeared, leaving us large limestone deposits.
Echinoderms, graptolites, bivalves and trilobites were all present.
Forests spread, and complex root systems may have altered the
Global climate. Whatever the cause, the first vertebrates
Hobbled onto the land.
Carboniferous Period (359.2 to 299.0 mya)
Attached filter feeders such as fenestellids, a common type of
Bryozoans, were abundant in this environment, as were brachiopods.
Clams made their first appearance in freshwater, and there was
Diversity in sharks and an increase in gastropod and bony fish. The
Environment supported fewer corals, crinoids, cryozoans, and bryzoans.
Fluctuations in sea level can be seen in the rocks as striped patterns from
Glaciation. Sea levels dropped, leading to an increase in terrestrial
Habitat. As the continents moved closer to forming Pangea, there was an
Increase of marine life in those shallow continental waters.
Permian Period (299.0 to 251.0 mya)
'Age of Dinosaurs' is what this period is called after a mass extinction.
Brachiopods, ammonoids, fusilinids, and other marine invertebrates, and
Conodonts fossils occur within such specific time frames that strata are
Determined by them and permit stratigraphic identification. In the
Early Permian, it appeared that the snapsids were to be the animals
Found most on land, but later on, the sauropsid group were most when the
'Great Dying' occurred. In as little as 100,000 years of Earth's
History, the majority of living species on the planet were wiped out.
Investigations showed evidence of catastrophic volcanic activity that
Justifiably would have initially caused rapid global cooling and
Killing of many species, and leading to increased glaciations.
Lowered sea levels and volcanic fallout would account for
Marine ecosystems in collapse due to much higher levels of CO2,
Not in the air, but in the oceans.
Triassic Period (251.0 to 199.6 mya)
At the beginning of the Triassic, land masses of the world were still
Bound together into the vast supercontinent known as Pangea.
Climate of the Triassic Period was influenced by Pangea.
Due to the low sea level, flooding of the continents did not occur.
Elevation of the continents were high compared to sea level.
Forests in Luarasia in beginning Triassic were dominated by conifers;
Gondwana was dominated by Dicroidium and Thinnfeldia. By the end, both
Hemispheres gave way to conifer and cycad vegetation.
Inevitably the climate changed as the continents drifted apart.
Jurassic Period (199.6 to 145.5 mya)
Apatosaurus and many other dinosaurs roamed the land in the Jurassic.
Brachiosaurus was another huge one. Small, fast bird-like coelurosaurs,
Ceratosaurs (horned reptiles) called Earth home. The famous
Diplodocus is a large long-necked Sauropod. Some plant life had
Evolved from Bryophytes, the mosses that lacked vascular tissue.
Floras were different from what we see today. Ferns, bennettitaleans,
Ginkgoes and cycads flourished in the Jurassic. Along with the large
Herbivores were some carnosaurs: Allosaurus and Tyrannosaurus rex.
Ichthyosaurus was a fish-shaped reptile in the sea. In August 2011,
Juramaia was discovered by scientists in China. This tiny animal is
Kinfolk to placental mammals, so has caused excitement.
Cretaceous Period (145.5 to 65.5 mya)
At the time of the Cretaceous, many modern groups of insects were
Beginning to diversify, and we find the oldest known ants and butterflies.
Ceratopsian and pachycepalosaurid dinosaurs appeared then. Some
Dinosaurs that learned to fly included the pterosaurs and Confuciusornis.
Extensive new coastlines came about from the continents moving apart.
Forests with oaks, hickories, and magnolias became common.
Grasshoppers and gall wasps appear, as well as termites and bees.
Half of the world's species went extinct about the time an asteroid hit.
Invertebrates became extinct in what was clearly a climatic event.
Eocene Epoch (55.8 to 33.9 mya)
An early horse ancestor, the dawn horse, is among the fossils found in
Both North America and Europe in the lower Eocene rocks.
Cattle and sheep are some of the artiodactyls fossils found.
Deer is another, and perissodactyls include rhinoceroses and tapirs.
Eocene Epoch marks the first appearance in the fossil record of the
First elephant-like animals and the early bats. There were whales and
Gastropods (a class of mollusks containing snails, slugs, and limpets) .
Oligocene Epoch (33.9 to 23.03 mya)
As a result of the cooling trend, habitats were directly affected.
Biotic provinces became more fragmented as sea dwellers
Capable of cooler temps went further from the warmer equator.
Deer, camel, elephants, cats, dogs, and primates began to dominate,
Except in Australia. Migration occurred between continents.
Falcons, eagles, hawks, and many families of rodents appeared.
Grasses and composites increased in abundance globally.
Horses experienced a period of diversification.
Miocene Epoch (23.03 to 5.332 mya)
Africa and Eurasia encountered significant tectonic movement.
Beginning in mid-Miocene, there was warming, followed by a
Cooling. It is considered responsible for diversification of plant life.
Desmostylia and other ocean-going mammals went extinct.
Eurasia and Australia grew increasingly arid. Europe kept its moist
Forests. Antarctica became isolated from the other continents.
Global ocean and atmospheric circulation were affected by that.
Hoofed mammals underwent a period of rapid evolution.
Pliocene Epoch (5.332 to 2.588 mya)
Asia's and India's tectonic plates collided, forming the Himalayas.
Basin ranges of Nevada and Utah were uplifted along with the
Colorado plateaus. Armadillo, opossum, and porcupines went north.
Dogs, cats, bears and horses migrated south. The beginning of the
Epoch saw numerous fluctuations in temperature.
Forests were replaced by grasslands. This favored grazing animals.
Generally the climate is thought to have been much warmer than today.
Hot times were replaced with cold and polar ice caps started to develop.
Pleistocene Epoch (2.588 mya to 11,700 ya)
Alternately, temperate zones were covered and uncovered by glaciers
Because of dramatically shifting climates and temperatures.
Camels and horses galloped across the plains of North America.
Diatoms, foraminifera, and plant pollen, were both abundant.
Ever larger land mammals appeared such as mammoths and mastodons.
Flowering plants, insects, mollusks, birds and mammals survive to this day.
Great teratorn birds with 25-foot wingspans stalked prey.
Homo sapiens came about, and humans spread through most of the world.
Holocene Epoch (11,700 years ago to today)
Another name for the Holocene is the Anthropogene, the 'Age of Man.'
By 8000 B.C., the cultivation of wheat, etc. had spread from the Fertile
Crescent through much of the Indo/European world.
Domestication of sheep, goats and cattle began at about the same time.
Extinction of the 'mega-mammals' caused Humans to switch to
Far smaller game and agriculture for their food supply.
Genetic modification of food started, and now is almost exclusive.
Habitat destruction is the leading cause of species extinction today.
Improved sanitation and medical care caused death rates to decline.
Judicial decisions against the death penalty further increased population.
Killing of police officers is increasing, while birth rates continue to climb.
Limiting factors in the environment provide natural balances to populations.
Monoculture has affected the composition and fertility of the soil.
Nuclear power has had some catastrophes, but is still an important tool.
Oil drilling and refinement have led to high migration of humans and pets.
Populations are rising with few restrictions, and are exponential.
Quakes in the earth are getting more frequent. Fracking is suspected.
Racial clashes around the world are a source of destruction and migration.
Species gone extinct in the Holocene are counted as at least 171.
Transportation across oceans has spread viruses and bacteria globally.
Uranium enrichment can be good, but can be the way to mass extinctions.
Virus mutations have led to super-viruses that are immune to antibiotics.
War has been the cause of mass migration, and smoke affecting climate.
X-rays save lives by alerting to medical problems that can be solved.
A Big Cheer You've done some very extensive research and put it down in a clever style. Good job! I'll buy a candy bar for anyone who can memorize it.
Thanks, Jim. I'll bet you're the first one to memorize it. Enjoy that candy bar!
Short? It took me half my life to read it! Just kidding. Once again you have amazed me with your astonishing array of facts, and brilliantly displayed in abecedarian form. Outstanding! A ten for sure.
It took quite a while to write it too. It was fun to learn that stuff. Thanks for your support.
This poem has not been translated into any other language yet.
I would like to translate this poem
Very incredible poem! What an amazing amount of X-cellent research! This must have taken Years to complete. Zillions of accolades for hard work and effort!
Thanks very much. No, only 3 or 4 days. Are you implying that I put a Y and a X at the end?